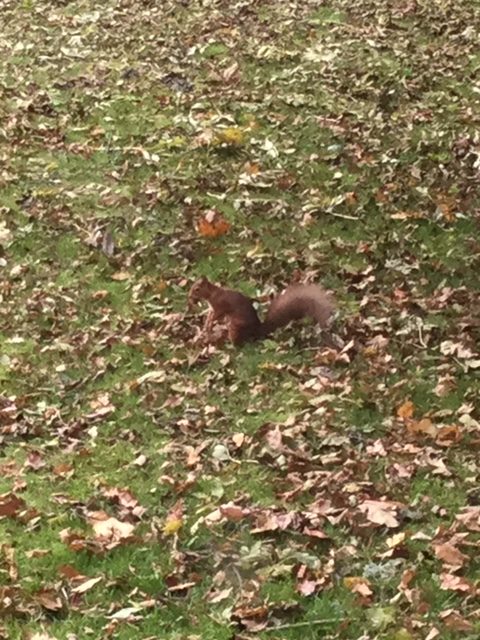
Red squirrel at Innerpeffray 
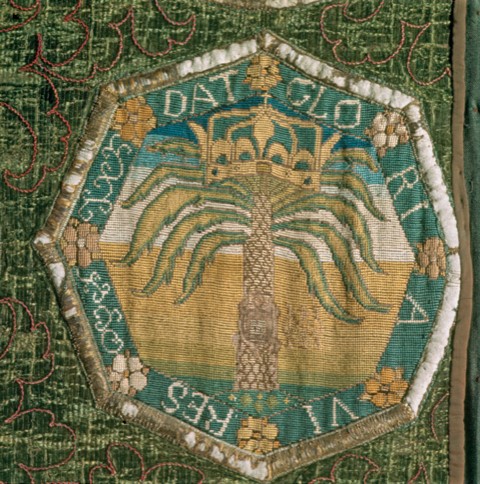
Embroidery of Squirrel Emblem 
Wither’s Emblem Squirrel
Not the least of the attractions of the green and leafy policies of the Library of Innerpeffray is the presence of red squirrels, a fact now emphasised by the embroidery kit depicting a squirrel on sale from the Library shop. The image is taken from the emblem book of George Wither (1588-1667): Wiki tells us that Wither had quite a colourful career, supporting the King against the Scottish Covenantors in 1639, and then Parliament in the English Civil War. However A collection of emblemes, ancient and moderne dates from earlier, having being published in London, by A.M. for Robert Allot, in 1635.
So what are “emblems” in the sense used here? Emblems were a pan-European genre of illustrated books which flourished particularly in the sixteenth and seventeenth century, and which reflected a world view in which thought was codified by visual and verbal associations, rather than by mathematics. To generalise wildly, the idea was to take word and text together, observe truth and draw a lesson, or amusement, or both: the combination of word and image would make the apprehension, conscious or unconscious, of the message clearer. We see the same thing at work in modern advertising. Emblems were not however restricted to books, or to Europe. More and more evidence of their use in architecture is emerging, as is their exploitation outwith Europe, for instance in South America, where indigenous imagery was used alongside European materials, notably in religious publications and buildings.
Scotland has a strong position in the emblem world. No less a person than Mary Queen of Scots used emblems for political ends in her embroidery; there are at least three important buildings with clear emblematic features: Pinkie Palace (a private building in Musselburgh), Caerlaverock Castle, and (closest to Innerpeffray) Culross Palace. The world’s best collection of emblem books is now in Glasgow University Library.

The Intrepid Squirrel
Innerpeffray’s single emblem book is, however, the copy of Wither used for the embroidery kit. We can gather the moral intent from the full title: A Collection of Emblemes, ancient and modern: quickened with metricall illustrations, both Morall and Divine: and disposed into lotteries, that Instruction, and Good Counsell, may be furthered by an honest and pleasant recreation. So the idea is to enjoy what you’re looking at and reading, but make sure you gain something from it. The thing about “lotteries” is potentially confusing for anyone reading the Innerpeffray copy, because the end of the book is missing, including a final leaf which incorporates two spinning pointers, which allow random selection (hence “lottery”) of particular emblems, and of connected moral lessons contained in supplementary verses, at the end of each of four parts. However, as it survives this copy can still be read as a “normal” emblem book, using the images and verses in conjunction.
There are two squirrel emblems: this particular squirrel comes from emblem 26 in Book 1.
The three parts have to be taken together: we have a pithy saying or motto at the top, a picture, and a longer verse. It is no accident that this emblem was chosen “during these strange times” of the corona virus:
With Patience, I the Storm sustaine,
For, Sun-shine still doth follow Raine.
Then comes the picture, an engraving of high quality by Crispin de Passe, lifted from an earlier publication by Rollenhagen, published in The Netherlands in 1611-1613, with its original motto: “Durabo” (I will endure/survive). We see the squirrel sitting out a rain storm, rather than lying “heartlesse in her Mossy dray”, as we read in the following long verse which spells out the moral points being raised. The lesson, stated in the last lines of the verse, is clear, reflecting the lines above the picture:
All Griefe shall have an ending, I am sure;
And, therefore, I with Patience, will Endure.
And the admonition to patience in adversity would be hammered home in the further verse which anyone operating the “lottery” (now missing in Innerpeffray, as noted above) would be directed to:
Thou, to Impatience, art inclin’d;
And, hast a discontented Minde;
That, therefore, thou mayst Patience learne,
And, thine owne Over-sights discerne,
Thy Lot (as to a Schoole to day)
Hath sent thee to the Squirrells Dray;
For, she instructs thee, to indure,
Till, thou, a better state, procure.
The odd thing is that peseverance in squirrels is not noted in classical sources, although Pliny notes that they take sensible precautions. This doesn’t really matter in terms of the message of this emblem.
The Wise Athenian Owl
The present writer has privileged information that a further embroidery will be on sale soon, again based on Wither, emblem 17 in Book 2. This time the image is one of four featuring owls.

Again there could be Covid 19 significance in its choice, for while the pithy saying at the top is pretty commonplace:
By Studie, and by Watchfulnesse,
The Jemme of Knowledge, we possesse.
we read in the longer verse the stern instruction that:
… in keeping Home, you do not spend
Your houres in sloth, or, to some fruitlesse end.
More Squirrels
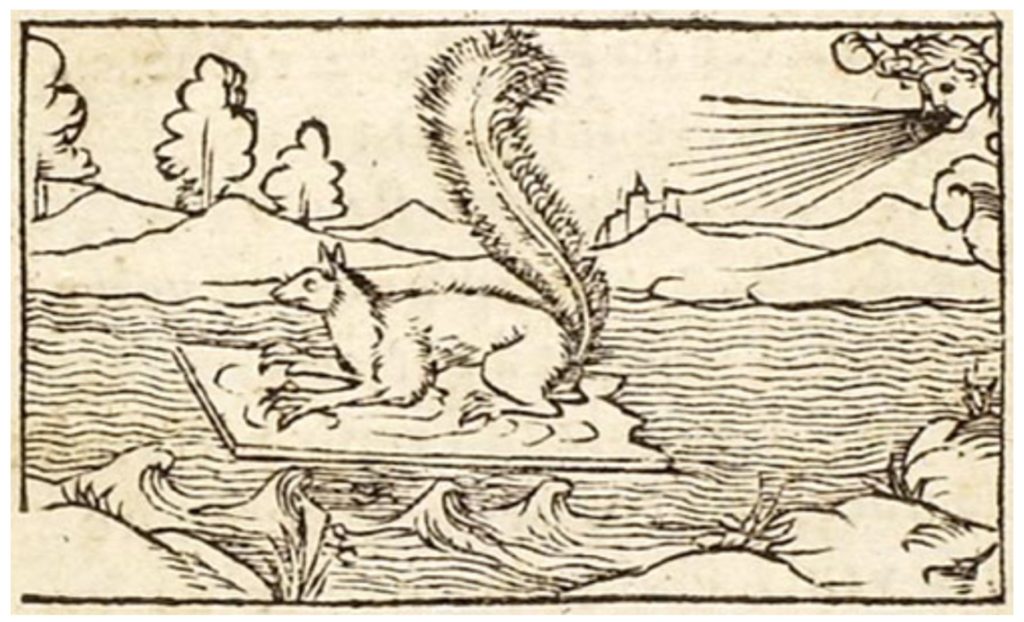
Other emblem images depict squirrels. This image dating from a very early emblem of 1540 shows a squirrel using its tail as a sail to cross a stretch of water, symbolising the need to use all means available to help oneself.

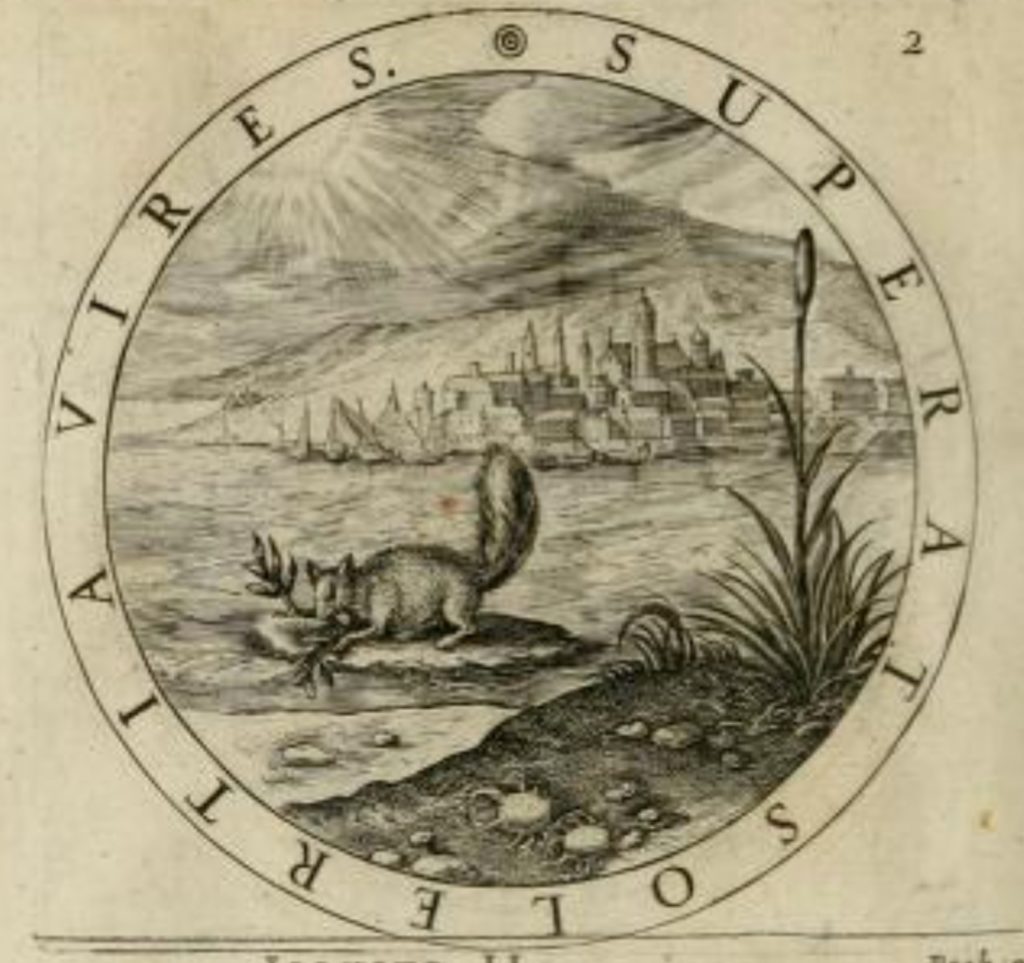
Wither uses the same motif, Book 3, Emblem 2:

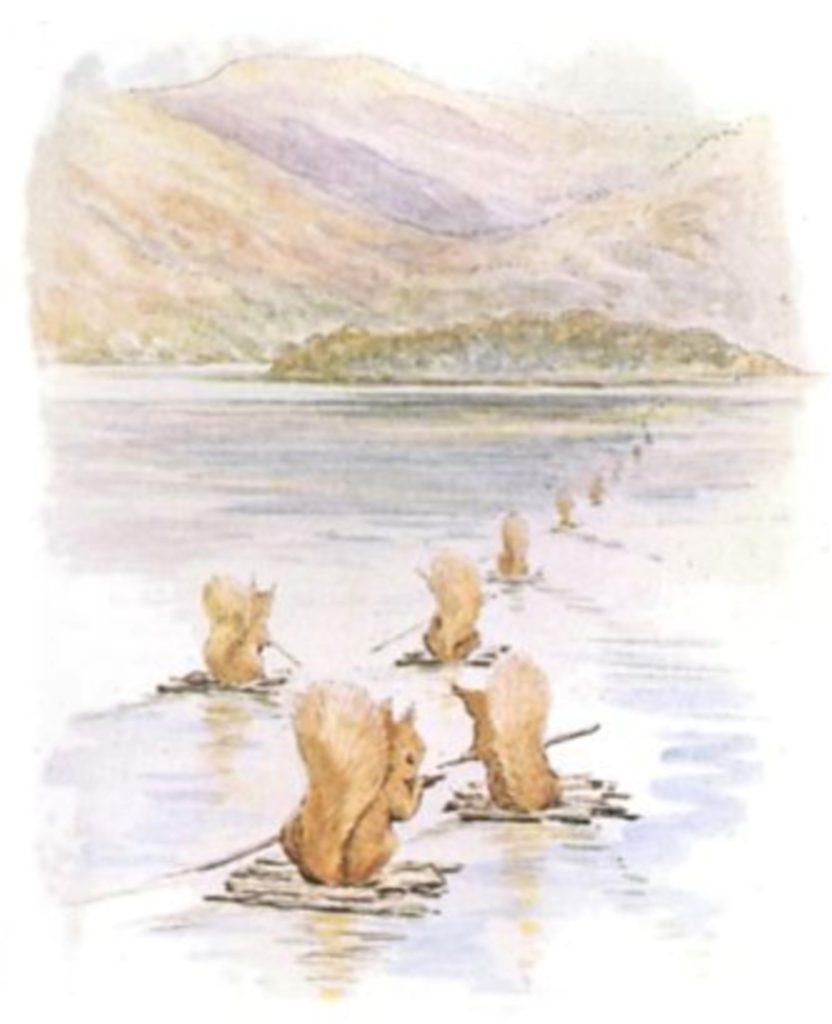
However, images of squirrels and owls need not be anchored in a quest for serious moral purpose. Probably the most well-known modern image of this motif will jump out at anyone who knows their Squirrel Nutkin!

And, lo and behold, we have an owl too:
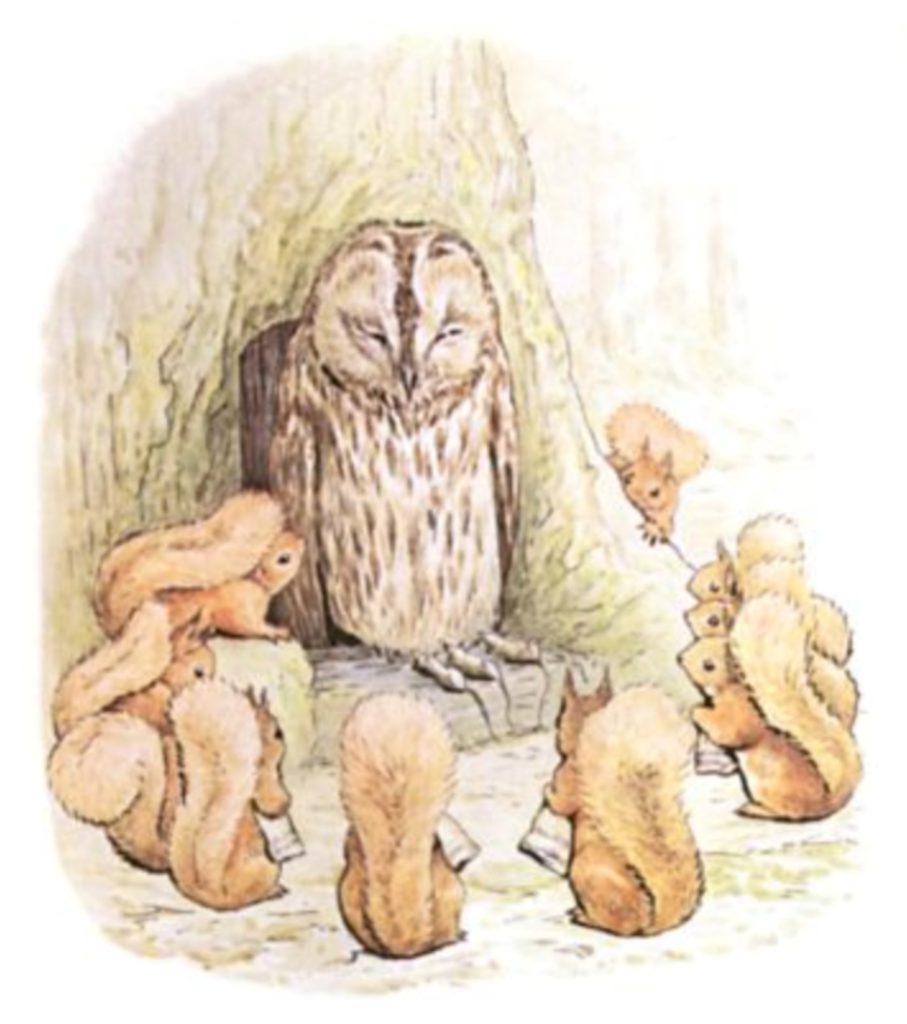

It is up to readers of this blog to determine the moral purport of these images, but the coincidence is charming, and I’d be moderately certain Beatrix Potter knew something about the tradition.
[For the record, the Innerpeffray Wither is recorded as having been borrowed seven times, between 1816 and 1887. The book has Lord Madertie’s signature: it is one of the original books collated at the founding of the Library.]
Links for more information and future reading…
Buy a Squirrel or an Owl embroidery kit, based on the emblems in our shop here
Complete copy of Wither:
https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uiuo.ark:/13960/t6d22jz4q&view=1up&seq=303
Stirling Maxwell Collection, University of Glasgow, Library: https://www.gla.ac.uk/myglasgow/specialcollections/collectionsa-z/stirlingmaxwellcollection/#
Caerlaverock:
https://www.historicenvironment.scot/visit-a-place/places/caerlaverock-castle/
Culross:
https://www.nts.org.uk/visit/places/culross
The 1540 squirrel: http://www.emblems.arts.gla.ac.uk/french/emblem.php?id=FCGa067
Squirrel Nutkin: